end tidal co2 range pediatrics
Br J Anaesth 2001. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al.

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar
End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 monitoring is a non-invasive continuous measurement of exhaled carbon dioxide CO 2 that offers real-time information about patients ventilation perfusion and metabolism 1234In ICU EtCO 2 monitoring ensures the integrity of the ventilator circuit and assists the titration of mechanical ventilation.

. 20 Bhende MS Thompson AE Orr RA. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring is not as reliable as arterial blood gas analysis for monitoring PaCO 2 however it may have a role in. Takahashi D et al.
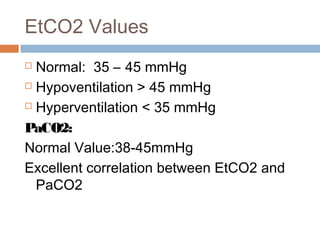
Arterial and end-tidal carbon dioxide difference in pediatric intensive care. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. The range of measures in which Pa co 2 and EtCO 2 are most similar.
End-tidal carbon dioxide E T CO 2 is the carbon dioxide CO 2 present in the airway at the end of expiration. End-tidal carbon dioxide CO 2 monitoring is useful in the prehospital setting emergency department intensive care unit and operating room. More than 95 of pediatric IHCAs in the US occur in intensive care units ICU 6.
Arterial to end-tidal carbon dioxide tension difference in children with congenital heart disease. Capnometry is the measurement and numerical display of the expired CO 2 and the capnometer is the machine that measures and displays the CO 2 in a numeric form. And End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide EtCO 2 by Hours Since Pediatric Intensive Care Unit PICU Admission.
Sullivan MD Niranjan Kissoon MD CPEy and Salvatore R. Physiologic dead space venous admixture and the arterial to end-tidal carbon dioxide difference in infants and children undergoing cardiac surgery. Although many do not have invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring during CPR another potential physiologic ap-proach to assess CPR is quantitative capnometry 347.
Indian J Crit Care Med. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading.
Et al End tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring in very low birth weight infants. Effect of tidal volume and end tracheal tube leakage on end-tidal CO2 in very low birth weight infants. Capnography provides valuable timely information.
We separately analysed the influence of age on the extent and incidence of negative PaCO 2 ETCO 2 differences. Capnography measures the amount of CO2 present at the end of exhalation end-tidal CO2 or ETCO2 displays a waveform that represents air movement through the respiratory cycle and continuously. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing.
End tidal Co2 ranges vary slightly from actual PaCo2 and can be affected by many factors depending on the condition of the patients lungs. Woodham and Railton for their comments on our work dealing with negative PaCO 2 ETCO 2 differences as reported with sidestream carbon dioxide monitoring during paediatric general anaesthesia 1. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
The relation between end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PETCO2 measured by infrared analysis and arterial carbon dioxide tension PaCO2 during exercise was systematically examined in five healthy. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. End-tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring in Pediatric Emergencies Kevin J.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Blood Pressure and End-tidal Carbon Dioxide Ranges during Aneurysm Occlusion and Neurologic Outcome after an Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Anesthesiology January 2019 A Comparison of the Respiratory Effects of Sevoflurane and Halothane in Infants and Young Children. Laboratory CPR studies indicate end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 during CPR is.
So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that. We would like to thank to Drs. Correlation and agreement with arterial carbon dioxide.
To determine the accuracy and precision of end-tidal CO2 monitoring in NICU patientsDesign. 2012 Vol 47 4 367-372. Endoscopic insufflation which was formerly conducted with air is being substituted with carbon dioxide CO2 in many pediatric clinics despite the fact that there is little published evidence on its usage in children.
Type of capnometry identified 91 of the instances when the arterial CO 2 pressure was between 34 and 54 mm Hg using an end-tidal range of 29 to 45 mm Hg. We previously established that using CO2 during esophagogastroduodenoscopy EGD in non-intubated children causes temporary increases in. 19 Toubas PL Duke JC Sekar KC McCaffree MA.
More Than Just a Number. Wang Y Goodman J Deep A. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in neonatesInfant 2008.
1 E T CO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. I suppose that the model eg.
Microphonic versus end-tidal carbon dioxide nasal airflow detection in neonates with apnoea. Non-invasive carbon dioxide monitoring Key points Harigopal S Satish HP. Utility of end-tidal carbon dioxide detector during stabilization and transport of critically ill children.
According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg.

End Tidal Oxygen Measurement White Paper Clinical View

Capnography By Craig Smallwood Rrt For Openpediatrics Youtube

Pdf Capnography In The Pediatric Emergency Department Clinical Applications Semantic Scholar

Pdf Capnography For Monitoring End Tidal Co2 In Hospital And Pre Hospital Settings A Health Technology Assessment Semantic Scholar
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar

Capnography In The Pediatric Emergency Department Clinical Applications
Etco2 In Non Intubated Patient A Must In Ed

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Pdf Delivery Room End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In Preterm Infants 32 Weeks

Characteristics Of The 21 Subjects Enrolled In Study Download Table

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Capnography In Pediatric Critical Care Unit And Correlation Of End Tidal And Arterial Carbon Dioxide In Ventilated Children

Exhaled End Tidal Carbon Dioxide As A Predictor Of Lactate And Pediatric Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar

Covidien Adult And Pediatric Colorimetric Co Detectors Pedicap6 Pedicap Easycapii6 Easycap Ii From 4md Medical